LPG gas
Liquefied gases are one of the petroleum products that are used all over the world today, such as city gas for cooking, and that is why it is interesting that
The two hydrocarbon gases butane and propane or their combination are called Liquefied Petroleum Gas or LPG. These gases are kept in liquid form and sometimes, other substances such as propylene and butylene are also present in the composition of these gases. Currently, the most important application of liquefied gases is heating and vehicle fuel. It is a colorless and volatile gas obtained by pressurizing, cooling and liquefying refinery gas or natural gas (including oilfield gas).
The main components of liquefied gas from refinery gas are:
- Propane
- propylene
- Butane
- Butene
The composition of liquefied natural gas obtained from natural gas is essentially free of olefins.
This gas is produced in refineries and is the result of refining crude oil and also a by-product of refining natural gas. Other uses of these gases include their use as coolants in cooling equipment such as refrigerators and air conditioners.
Liquefied gas is a flammable substance that will explode when exposed to an open flame when the air content reaches a certain concentration range.
History of LPG gas discovery
In 1892, Holland was the first to use natural gas to test and obtain liquid methane
He created the theoretical basis of oil gas liquefaction.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Dr. Walter Snelling conducted a stability test on gasoline and he found that the gas volatilized by gasoline is liquid under certain conditions of temperature and pressure and successfully extracts propane and butane from natural gas.
Germany, the United States, Japan, France, Italy, and some Eastern European countries also produce and use LPG.
During the past half century, with the development of oil resources and the development of the refining and chemical industry, not only has the rapid expansion of liquefied gas occurred in countries with rich oil resources;
Moreover, some countries with poor resources have also produced large amounts of liquid gas.
LPG gas is currently produced in all continents. North America and the Middle East are the largest LPG producers, followed by some Asian regions. Africa produces less than 10% of global production. In 2008, the world consumption of LPG was 230 million tons. In 2012, consumption reached 265 million tons.
What are the main features of LPG?
May be you have been asked what are the characteristics of LPG?
We will answer this question in this section.
- LPG is a mixture of light hydrocarbon compounds.
- It mainly consists of butane (C4H10) or propane (C3H8) or a mixture of both.
- Both gases are colorless and odorless at room temperature.
- The temperature of propane is -42°C and butane is -0.5°C.
- Under moderate pressure or in cooler conditions, LPG turns into a liquid state.
- LPG gas, which is used in household cylinders for cooking, generally has more butane than propane;
- Because the amount of fuel per kilogram of butane is higher than propane and it liquefies under much lower pressure than propane.
- When liquefied under pressure, the volume of butane and propane is reduced to about 1/260 of the gaseous state.
- The specific heat value of LPG is about 46 MJ/kg or 12.78 kWh/kg, depending on the composition of LPG.
- Liquid gas is heavier than air and can reach the top of the atmosphere. This may lead to LPG-‘lakes’. In order to detect the leakage and reduce the risk of explosion, adding bad smell to the gas is done.
What are the advantages of using LPG?
As a general fuel, LPG has its obvious advantages:
- Comprehensive use of oil resources
- The equipment for its transmission and distribution system is simple. (Saving investment)
- Easy to use and environmental protection: liquefied gas is almost free of any combustible components. After complete combustion, it is basically odorless and non-toxic, does not produce ash, is clean and hygienic, and protects the environment.
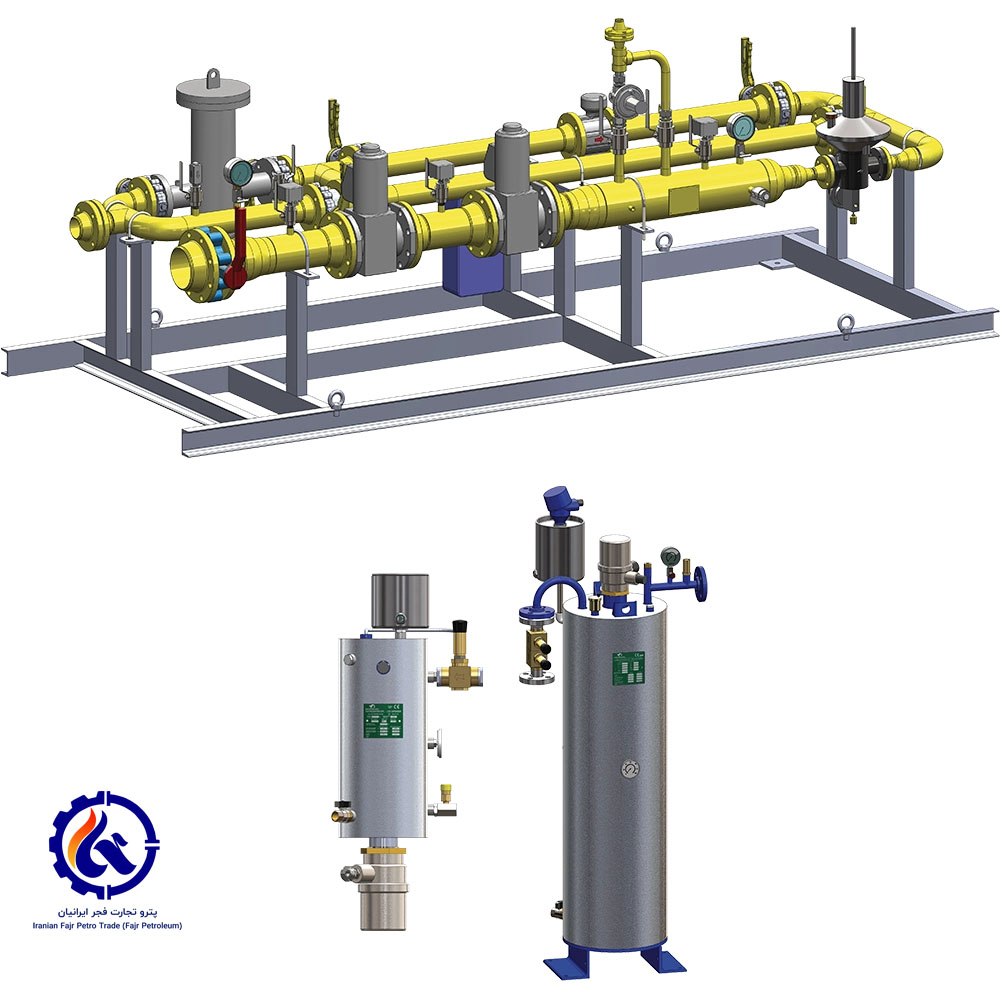
- Flexible supply: In order to facilitate storage and transportation, this method is usually under pressure or liquid cooling. Reducing the volume of liquefied gas to 1/250 to 1/300 of the original volume is under pressure inside the container, it is easy to transport and can be used by urban and rural customers. Pipelines can be used to supply gas in areas where residents are concentrated, and LPG tanks can be used in areas where residents are scattered; therefore, its distribution is very flexible
- High calorific value: the calorific value of liquefied gas is three times that of natural gas and more than six times that of synthetic gas.
- Suitable for long distance transportation.
Dangerous properties of liquid gas
- In this section, we will discuss what are the disadvantages of LPG gas and what points should we pay attention to when using it.
- Avoid possible risks.
Explosive properties of liquid gas
- The first and biggest disadvantage of LPG is its explosiveness.
- In general, when an LPG accident occurs, an explosion will occur and it will explode before burning.
- The main reason is that the calorific value of LPG is relatively high.
- The calorific value of liquefied natural gas alone is several times higher than that of ordinary coal gas.
- Therefore, when a safety incident occurs in liquid gas, an explosion appears.
Flammable properties of liquid gas
- Liquid gas is one of the main components of oil. These components are all common hydrocarbon compounds and
- The biggest characteristic of hydrocarbon compounds is their flammability.
- In addition, the ignition point of these hydrocarbon compounds in the liquid gas composition is very low, which can easily cause combustion.
Toxicity of liquefied gas
- Liquid gas is a poisonous gas, but the risk of this poisoning depends on some conditions.
- Only when the concentration of liquefied gas in the air is more than 10%, it causes poisoning of the human body.
- When the human body is exposed to such a poison, vomiting, nausea and even coma occur, which can cause great harm to the human body.
Velocity and volatilization of liquefied gas
- The flow of LPG is very easy, whenever there is a leak, the LPG will come out of the storage.
- In addition, under normal conditions, 1 liter of LPG produces about 350 liters of volatile gas after being discharged.
- These gases burn when they come into contact with electricity and cause serious fires.
What is the use of LPG gas?
The use of liquefied gas as a fuel has been widely used for the following reasons:
- Its high heat value
- No smoke generation
- No carbon residue
- Easy to use
- Its use in people’s lives
In addition, liquefied gas is also used for the following purposes:
- Metal cutting
- Cooking agricultural products
- Roasting in industrial ovens
- As a raw material for petrochemicals
- Cracking of hydrocarbons to produce ethylene or steam reforming to produce synthetic gas
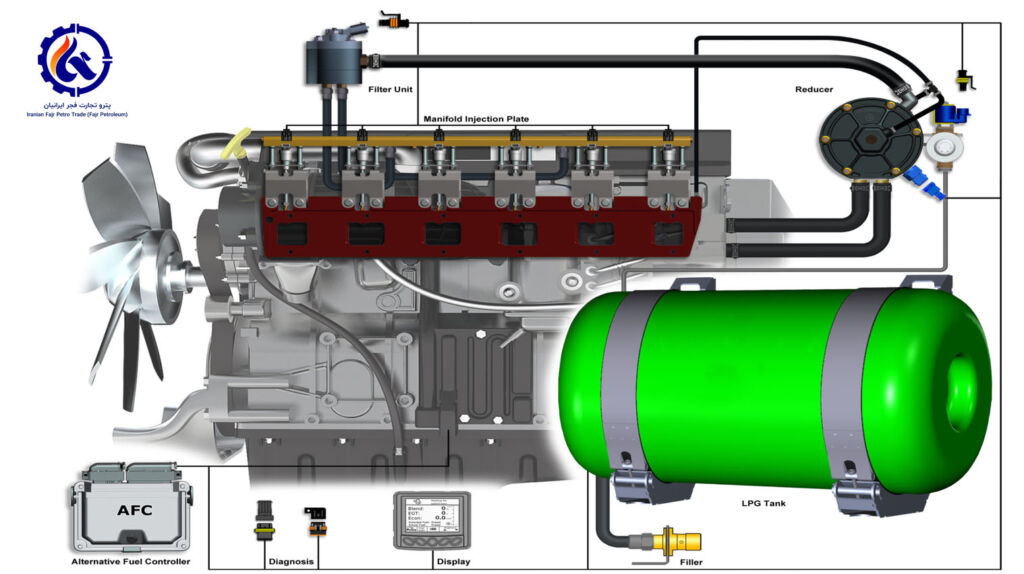
As a fuel for combustion engines, LPG gas is used as a fuel for cars
LPG is commonly called auto gas when used as a fuel for vehicles with an internal combustion engine.
It can also be used for fixed ICE installations such as generators.
LPG is a fuel gas.
LPG gas is also known as propane or butane.
A flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases used as fuel in vehicles.
How LPG works in an engine is basically the same as an internal combustion engine with gasoline.
The engine block, pistons, spark plugs, ignition system, lubrication system, and electrical system all run on LPG fuel.
It consists of propane, butane, or a mixture of the two, and is also called liquefied natural gas (LNG).
- Domestic and industrial
- Synthetic plastics production
- Synthetic rubber
- Production of synthetic and medicinal fibers
- Explosive materials
- Color
- And…
Quality control mostly focuses on evaporation residues and sulfur content and sometimes the olefin content must be controlled as well.