Crude oil and its applications in life
The English word PETROLEUM is derived from the Latin language and means stone oil. Crude oil or petroleum is one of the most widely used natural materials in human life, which is known as the most consumed liquid after water and is used in the production of many products consumed by humans in various fields. Crude oil is garlic brown or dark green in the upper layers of the earth’s crust. It is a thick and flammable liquid that contains a complex mixture of various hydrocarbons.
Crude oil compositions
Crude oil, which includes various compounds, is in the form of solid, liquid and gas hydrocarbons. At the temperature and pressure of the earth’s surface, light hydrocarbons including methane, ethane, propane and butane exist in gaseous form, while heavier hydrocarbons exist in liquid or solid form. In the underground, the solid, liquid or gaseous states of hydrocarbons are related to their phase diagram.
During the production of crude oil in oil wells, some gas dissolved in crude oil is also produced, and when it reaches the surface of the earth, due to its lower pressure, this gas loses its solubility. This type of gas is called companion gas. Of course, it should be said that in gas wells, the main product is natural gas. Natural gas under high pressure and temperature includes heavier hydrocarbons such as pentane, hexane and heptane. But on the surface of the earth, these heavy compounds are separated from gas in liquid form. This type of gas is called condensate gas.
The ratio of hydrocarbons in light crude oil is different in different oil fields. This ratio decreases to about 97% in light oil tanks and less than 50% in heavy oil tanks. Crude oil mostly contains alkanes, cycloalkanes and aromatic compounds. There are other elements in the composition of crude oil, including nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur and metals, which are different in each formation. In general, the relative amounts of these compounds are given in the table below:
Crude oil has an oily state and can be seen in solid (oil bitumen) and liquid forms.
To get familiar with some common terms, we review the following:
- If oil accumulates in a sedimentary layer, it is called an oil pool.
- An “oil field” is obtained from the sum of several oil basins.
- Porous rock that contains oil and has the ability to produce oil is called reservoir rock. Refinement of crude oil is the first step in the series of steps that take place in order to transform oil into more than 2500 different products. The crude oil output from the well is sent to the refinery where the refining process is carried out. The operational purification process is complex and includes several different steps.
Name of the compound | Percent |
|---|---|
Carbon | 80 to 83 |
Hydrogen | 10 to 14 |
Nitrogen | 0/1 to 2 |
Oxygen | 0/05 to 1/5 |
Sulfur | 0/05 to 6 |
Metals | Less than 0.1 |
Follow us to learn more about crude oil refining processes:
Desalination
Crude oil initially contains many undesirable substances such as sand, mineral salts, drilling mud, polymer, etc. These additional materials can be completely dissolved or in the form of crystals in suspension in water with oil. The main trick used for this purpose is washing the salts with water.
- Desalination steps of crude oil
- Injecting and dispersing water
- Water-in-oil emulsification
- Emulsion spreading in the electrostatic area
- Electrostatic coagulation
- Separation of water droplets
The set of operations and processes mentioned causes the salt to dissolve in the water droplets and separate them from the oil. Finally, the water droplets are removed from the oil flow using a separator system.
Crude oil distillation
At this stage, in the atmospheric distillation tower, side stripers, feed desalinizer and furnace act as the main components. Generally, five main products are obtained from the atmospheric distillation tower, which are: gas + naphtha, kerosene (white oil), light petroleum gas, heavy petroleum gas and atmospheric residue.
Other products that are obtained from this tower include gasoline, jet fuel and diesel, which are produced from naphtha, kerosene and petroleum gas. Among the distillation products, naphtha and kerosene have a higher value compared to heavier compounds such as oil gas and atmospheric residue.
Vacuum Distillation
Due to cracking reactions, hydrocarbons can be heated up to 400 degrees Celsius. Also, the clogging of pipes due to soot and equipment will increase operating costs and reduce unit efficiency.
Therefore, the distillation of heavy components, which are called atmospheric residues, is carried out at low pressure (close to vacuum). The boiling point of hydrocarbons is lowered due to lower pressure. For this reason, they perform the distillation operation at a lower temperature. The area where this operation is carried out is called Borj Tagheer Khola.
The products removed at this stage include light and heavy vacuum gas, which are used as feed for cracking units or lubricating oil processes. The output of the vacuum tower is also used for the production and processing of bitumen.
Thermal cracking
Thermal cracking involves a chemical cracking process followed by the use of physical principles (differences in boiling point) to achieve the desired products.
The products of this process are: gas + naphtha, oil gas and cracking residues
Operational conditions
To destabilize larger hydrocarbons, a temperature of about 450-500 degrees Celsius and a pressure of 2-3 times is considered.
Hydrogen purification
Many crude oils contain a high percentage of sulfur, which is considered an undesirable combination and greatly reduces the quality of the products produced. For this reason, the products produced from atmospheric and vacuum towers are purified using hydrogen so that the sulfur is finally separated from the oil and removed. The hydrogen used for purification is supplied from the reforming unit.
The commercial production of crude oil was initially for lighting homes. However, with the discovery of other properties of oil, this material became a strategic commodity, without its continuous supply, global stability and security face a serious risk.
As mentioned, crude oil is composed of carbon and hydrogen elements and is one of the types of hydrocarbons. And according to hydrocarbon compounds and its sulfur content, it is classified into light and heavy, sour and sweet crude oil.
Types of crude oil
Brent Crude Oil
Brent crude oil is one of the most familiar types of crude oil, which is used as the basis for pricing many types of crude oil in global markets. Brent crude oil is a combination of oil extracted from the Brent and Ninan channels in the North Sea, which is transferred to the Salum oil terminal and the largest export port of the North Sea in the UK through a pipeline network and loading is done there. Brent mixture has an API grade of more than 38 and its sulfur content is 0.41%, so it is classified as light and sweet crude oil.
Mars crude oil
Mars crude oil is one of the types of heavy and sour crude oil that is produced in America and the Gulf of Mexico and is loaded and exported at closely port. The API grade of March crude oil is 29 and its sulfur content is 1.9%. The production rate of mixed crude oil in March is estimated from 150 to 230 thousand barrels per day. One of the biggest producers of this crude oil in the world is Shell.
Minas crude oil
Minas crude oil, also known as Sumatra Light, is one of the leading crude oils in the Asian market, which is produced in the dry areas of the Indonesian island of Sumatra and is exported from the port of Dumai. This crude oil with an API grade of 35.8% sulfur is considered to be light and sweet oil. The export shipments of this crude oil are from 500 to 700 thousand barrels per day. The daily production of Minas crude oil is estimated to be more than 400,000 barrels.
Murban crude oil
Murban crude oil is considered among light and relatively sweet crude oils with an API grade of 39.3 and the presence of 0.8% sulfur. This crude oil is produced and loaded in the United Arab Emirates. The amount of crude oil produced in Murban is estimated up to 1.5 million barrels per day.
Tapis crude oil
Tapis crude oil with an API grade of about 46% and a sulfur content of 0.03% is produced in the Terengganu offshore area of Malaysia. It should be noted that unlike Brent crude oil, this type of crude oil is not traded in the oil market, but it is considered one of the leading types of oil for pricing in the Asian region. Due to its extensive trade relations with the Asian region, Australia uses the Tapis crude oil price as the basis for pricing its imported crude oil and even its petroleum products.
Different applications of crude oil
When talking about oil and its uses, most people think of fuels like gasoline or diesel. But the use of crude oil and its products is not limited to these cases only, but includes a wide range of products in various fields from technology to economy, industry, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, food industry and household appliances.
Some of the uses and applications of crude oil are:
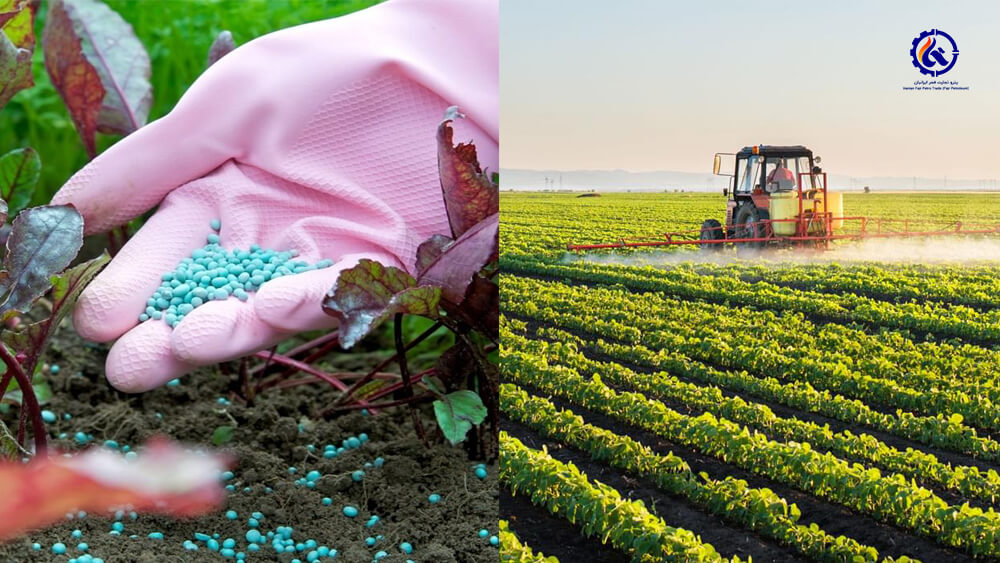
Agriculture
One of the most important uses of crude oil in the agricultural industry is the production of chemical fertilizers. Crude oil is used to prepare ammonia, which is a source of nitrogen in agriculture and is obtained during the Haber process.
In addition, crude oil is used in the production of most of the pesticides used in the agricultural industry. Crude oil is also used to run agricultural machinery.
Paints, detergents, etc.
Some aromatic hydrocarbons in crude oil include toluene, benzene, and xylene, which are used in the production of products such as paints, synthetic detergents, and fabrics.
The raw materials for making polyurethanes are benzenes and toluene, which are used in surfactants, oils and even wood polishing.
Sulfur is the main component of sulfuric acid, which is obtained from crude oil.
Plastics, painting colors, etc.
Plastic is one of the essential and important elements needed in today’s modern life. The uses of these products range from computer monitors to nylons and citrofoams, which are produced in factories and from crude oil.
The polystyrenes used in making polystyrene foams and polyvinyl chloride or PVC are both industrial products of the post-World War II era and are derived from crude oil.
Nylon, which is used in everything from socks to food packaging, car wheels, and even car engines, is considered the most successful crude oil-based plastic.
Plastics are often obtained from olefins, which include ethylene and propylene (from the alkene family).
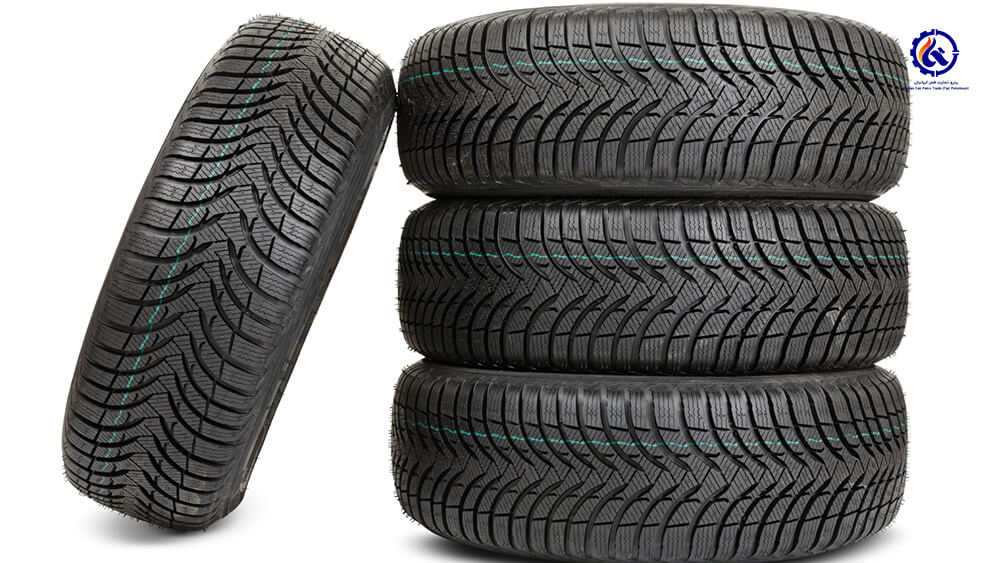
Car tires
Until the beginning of the 20th century, all rubbers were made from natural plant elastomers, and the need for synthetic rubber was relatively low until the Second World War. But during the world wars, due to the embargo on natural rubber from South America, the need to produce synthetic rubber increased.
Synthetic rubber is one of the products of butadiene, which is considered one of the main pillars in the petrochemical industry.
Pharmaceuticals
Mineral oil and Vaseline are crude oil products that are used in many topical creams and ointments.
Tar shampoo is one of the petroleum products used to treat psoriasis and dandruff. Also, most of the drugs have complex organic molecules that are based on simpler and smaller organic molecules and most of them are obtained from crude oil.
Transportation
The entire transportation system of the world is dependent on crude oil and this material has created a huge revolution in the road, rail, and water and air transportation system. As you know, gasoline and diesel, which are the main sources of energy for all modern vehicles, are both derived from crude oil.
Electricity production
The main source of power generation is in the field of crude oil industry and diesel is used in gas turbines to generate electricity.
Heating and lighting
Heavier oils are used in central heating devices for shops, offices and homes. Oil is also used to produce electricity, which the industrial and home lighting system depends on. Lighter oils such as kerosene are also used for domestic purposes.
Lubricant
Lubricants and greases are used in various devices, especially transport vehicles and industrial machines that consume a lot, all of which are produced from crude oil.
Petrochemical industries
Both chemical and petrochemical industries use petroleum products as raw materials. Petroleum products are widely used in the production of chemical fertilizers, synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber, nylon, plastic, pesticides and insecticides, as well as perfume, paint, carbon black, sulfur, etc. The production of these materials requires crude oil.